Sunburst Sales Radiant Floor Q&A
![]() FREE Quote - Fill out the Radiant Floor Worksheet.
FREE Quote - Fill out the Radiant Floor Worksheet.
Radiant Floor Heating Q & A
- What are the advantages of radiant heating?
- What is hydronic radiant floor?
- How is radiant heat different from other types of heating?
- Are many people using this type of heat?
- Why are so many people utilizing radiant heat?
- What about efficiency?
- What types buildings is radiant heat used in?
- How does radiant floor compare with overhead convectors?
- How about heat loss when I open my overhead doors?
- Do I need to insulate under the slab?
- Does the tubing go directly into the concrete?
- In a shop or garage, how do I finish the transition between floor and foundation?
- Can I install the tubing on upper floors?
- How much insulation do I need under the sub-floor?
- Can I use a water heater to heat my building?
- What parts do I need to do the job?
- What type of tubing is used?
- How do I get help with my project?
- How do I order?
Advantages
- Comfort - Warm at the floor and coolest near the ceiling. No drafts.
- Energy Efficient - Save up to 30% over forced air. Set thermostat 6-8 degrees lower and still feel warm.
- Quiet - No fans or blowers.
- Clean - Less dust movement. Ideal for people with allergies.
- Invisible - Out of sight plus no restrictions on the placement of furniture.
- Safety - Dry floors in shops, garages and warehouses.
- Flooring - Works well with a wide variety of carpet and flooring.
What is hydronic radiant floor?

It is an energy efficient heating system that works by circulating hot water through tubes in or under the floor.
How is radiant heat different from other types of heating?

The majority of heating systems in use are forced air with duct by convection. They heat the air, and then the air circulates around and heats the objects in the room.
The best example of radiant heat is the sun. It gives off electromagnetic waves that travel through space without heating it. Only when the waves strike an object, like your face, the waves are transformed into the heat you feel. Radiant heat works like that. It produces heat when waves strike the objects in the room. The objects then heat the air.
Are many people using this type of heat?

Radiant is the fastest growing type of heat in the United States and has been used extensively in Europe for some time.
Why are so many people utilizing radiant heat?

Several reasons. Probably the most common reason is comfort. The heat is closest to the floor where it is needed most. The Chart below shows the differences in room temperatures with radiant floor and forced air.
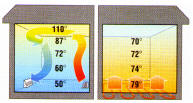 |
Notice the temperature range difference with forced air heat. Plus, no fans or blowers make radiant floor quiet and clean! No excessive dust or noise! |
What about efficiency?

Savings over forces air can be over 30%. This is partially due to the fact that the heat stays closer to the floor and less heat is lost through the ceiling. Plus, many people set their thermostats 6 – 8 degrees cooler and still feel warm.
What types buildings is radiant heat used in?

Commercial
- Repair Shops & Utility Sheds
- Greenhouses
- Airplane Hangars
- Snowmelt
Residential
- New Construction
- Additions
- Remodeling
- Garages
How does radiant floor compare with overhead convectors?

Radiant floor has many advantages over convectors.
- Appearance & Cleaning – radiant floor is out of sight. No cleaning required.
- More heat is on the floor and under machinery.
- Never worry about burning off the top of tall equipment.
How about heat loss when I open my overhead doors?

Since the heat is in the floor, it is affected less by overhead doors than hot air unit heaters would be. Your entire slab plus the objects in your building are warm, so when the door is closed these objects are immediately radiating heat. With a hot air system most of the air is lost and the system has to basically start over.
Do I need to insulate under the slab?

Yes, definitely. Unlike hot air, which rises, radiant heat goes in all directions. You should have a minimum of 2” perimeter insulation as will as a minimum of 1” under the slab.
Does the tubing go directly into the concrete?

There are basically three different methods for putting the tubing in or under the slab. Insulation recommended is closed cell polystyrene in a minimum of 1” thickness. Vapor barrier is a 6 mil plastic.
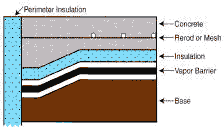 |
Tubing is tied to rerod and is installed in the center of the concrete. Tubing is attached to the rerod with plastic ties. |
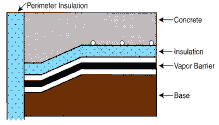 |
Tubing is attached to insulation with screw clops and installed at the bottom of the concrete. |
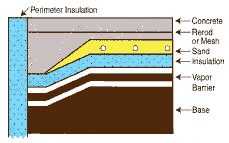 |
Tubing is placed in approximately 2” of sand below the concrete slab. It is attached with screw clips to the insulation. |
All three of these systems work equally well. Choose whichever system is easiest to layout for your situation. Placing the tubing in the sand may make it easier to trowel concrete because the water can go into the sand.
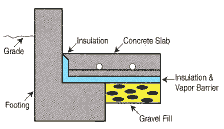
In a shop or garage, how do I finish the transition between floor and foundation?
You can install the insulation about an inch below the surface so the concrete will float over it or you can cut the edge on a 45-degree angle. |
 |
Can I install the tubing on upper floors?

Of course. There are many different methods of installing tubing on subfloors. It is very important to have the right amount of tubing and proper layout for these types of installations.
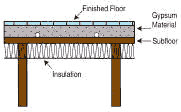 |
Tubing is attached to the top of the wood subfloor. Lightweight concrete or gypsum is poured over it. Finish flooring or carpeting is installed over concrete. |
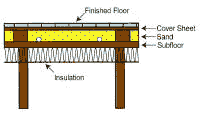 |
Wood strips or sleepers are glued and nailed to the subfloor. Tubes are placed between the sleepers. Gaps between sleepers can be filled with sand to increase heat-holding capacity. The floor is then covered with a plywood cover sheet. Finish flooring or carpeting is installed over plywood cover. |
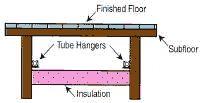 |
Tubing is attached to joists underneath the subfloor. By installing the tubing on the sides of the joists, tubing damage can be avoided from nails or screws placed in the floor. Installing the tubing between the joists is the least desirable method of installation. There is no mass to hold the heat and radiate from. The R-Value of the floor covering becomes very critical with this method. It’s also more difficult to install. |
How much insulation do I need under the sub-floor?

Generally, if the floor is over an unheated basement use R-19. If the floor is over a heated basement use R-13. When installing over a crawl space use R-30.
Can I use a water heater to heat my building?

This is a popular idea and may work for you bur it depends on how much heat your building requires. Water heaters are limited on BTU output. Sunburst Sales can run a heat loss calculation for your project. From this, we can advise you of your needs.
What parts do I need to do the job?

Tubing
We recommend keeping the maximum length for each loop between 250 -300 feet when using 1/2" ID PEX-AL-PEX. A large area will require several loops.
Protective Sleeve
These are the distribution points from the heat source. Ideally they are centrally located in you building. Return manifolds have built in balancing valves.
Adapters
These are used to connect the tubing to the manifold.
Manifold Mounting Bracket
Use to mount manifolds to the wall.
Pump
Sunburst Sales handles Taco and Grundfos brand pumps. We have several different models and sizes. The most common pump for radiant floor applications is a zone circulator, which has a low voltage relay built in. It can be wired directly to your wall thermostat.
Isolation Pump Flanges
These flanges have built in ball valves, that can be turned off with an Allen wrench, so that you can remove the pump without draining the system.
Air Pressurizing Assembly
This attaches to the return manifold. It will allow you to put pressure into the tubing before you pour concrete. It also helps to bleed air out of the system when it is being filled.
What type of tubing is used?

Sunburst Sales uses Pex-Al-Pex. Pex-Al-Pex is a cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) tubing with an aluminum oxygen barrier. The tubing is going to be in your floor forever, so we believe in using the best product available. The unique construction of the Pex-Al-Pex tube combines the best of both metal and plastic.
How do I get help with my project?

Call, mail or fax your information to us. We can work off your blueprint or a sketch. We need to know dimensions and some basic information like room sizes etc. Fill out the Radiant Floor Worksheet and submit it to us. Based on your information, we will provide you with a detailed list of recommended components and the price delivered to your door.
How do I order?

Email Greg at:
Get a FREE Quote - Fill out the Radiant Floor Worksheet.
